Background
We have our staging and production environments hosted on Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS). If you are not familiar with AKS, it’s the managed K8s service provided by Azure.
By default, AKS uses a managed remote Azure Storage for the OS disks of the nodes, whereas if you use ephemeral OS disks, then they are created on the local virtual machine (VM) storage.
Why use ephemeral OS disks?
With ephemeral OS disks, we see lower read/write latency on the disks of AKS nodes as the disks are locally attached to the VM.
You will also get faster cluster operations like scaling or upgrading clusters, cause now the re-imaging and boot times are faster due to the disks being locally attached to the VM.
Also we do not incur any additional storage costs for OS disks with ephemeral OS disks.
These are ideal for stateless applications and workloads, but not suitable for stateful applications as the disks are ephemeral.
What to consider while using ephemeral OS disks?
We can store ephemeral OS disks on VM’s OS cache disk or temporary storage SSD. So the size of the ephemeral OS disk should be less than or equal to the size of the OS cache disk or temporary storage SSD of the VM node size.
Since VM’s OS cache disk and temporary storage SSD are determined by the VM node size, we need to select the right VM node size for our nodes.
For example:
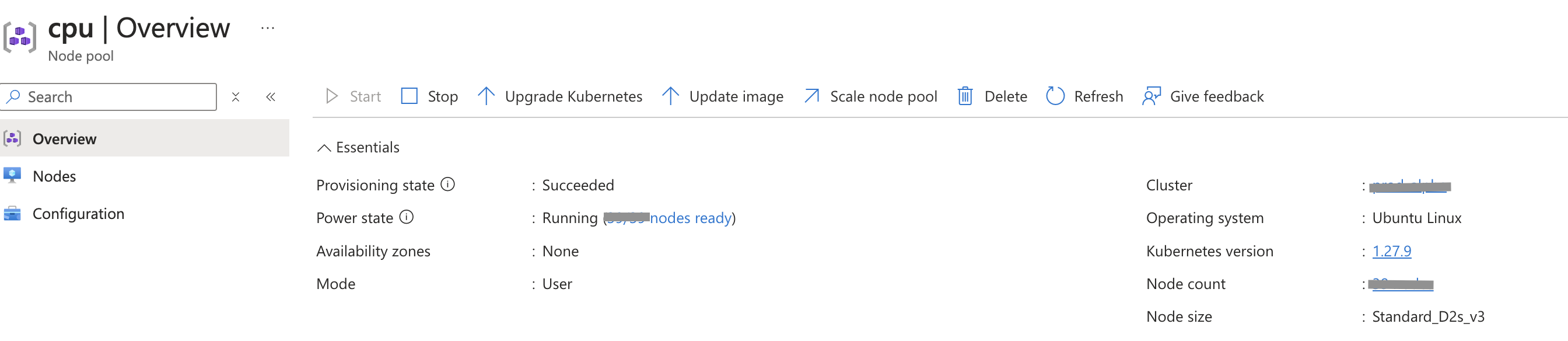
Let’s say our cluster node size is Standard_D2s_v3 for the node pool (nodes of the same configuration are grouped together into node pools. These node pools contain the underlying VMs that runs our applications) as shown above.
Now let’s check the size of the OS cache disk and temporary storage SSD for this node size.
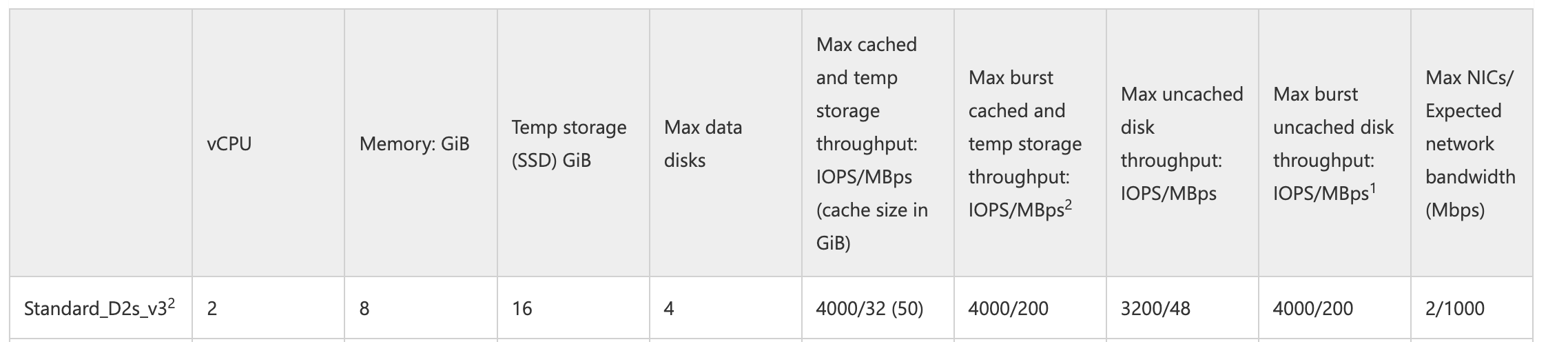
So here, as you can see the temp size is 16GB and OS cache size is 50GB. So our max ephemeral disk size should be less than or equal to 50GB.
The max ephemeral disk size is limited by the node size that we choose.
Note: Check your node size’s OS cache disk and temporary storage SSD size here.
Migration
We already have a node pool with Managed Disks and we want to migrate to Ephemeral OS Disk.
We won’t be able to change the OS disk type of the existing node pool, so we need to create a new node pool with OS disk type as Ephemeral and migrate the existing workloads to this new node pool.
Let’s say the existing node pool is nodepool-1 and we are creating a new node pool with Ephemeral OS Disk as nodepool-new.
The entire migration needs to be done without any downtime.
We are using Terraform to manage our AKS clusters.
- First we need to create the new node pool
nodepool-newwith OS disk type asEphemeral OS Disk.
resource "azurerm_kubernetes_cluster_node_pool" "d2s_v3_node_pool_new" {
name = "nodepool-new"
kubernetes_cluster_id = azurerm_kubernetes_cluster.default.id
enable_auto_scaling = true
os_disk_type = "Ephemeral"
min_count = var.d2s_v3_node_count
max_count = var.d2s_v3_node_max_count
vm_size = "Standard_D2s_v3"
os_sku = "AzureLinux"
os_disk_size_gb = 50
vnet_subnet_id = azurerm_subnet.default.id
}
As seen above, to enable ephemeral OS disk, we set os_disk_type to Ephemeral and os_disk_size_gb is set to 50GB which is equal to the size of the OS cache disk of Standard_D2s_v3.
Note: os_disk_type defaults to Managed if not specified.
- Next step is to safely migrate the existing workloads in
nodepool-1tonodepool-new.For this, we will first need to cordon the nodes in
nodepool-1so that no new pods are scheduled on them.Then we drain the nodes in
nodepool-1so that the existing pods are rescheduled on to the nodes innodepool-new.This was done manually through a script using
kubectl.- Get all the nodes in
nodepool-1.
kubectl get nodes -n <namespace>- Cordon the existing nodes from
nodepool-1.
kubectl cordon <node1> <node2> ...- Drain the nodes from
nodepool-1.
To ensure the successfull draining of nodes, we need to ensure that PodDisruptionBudgets allow for atleast one replica to be moved.
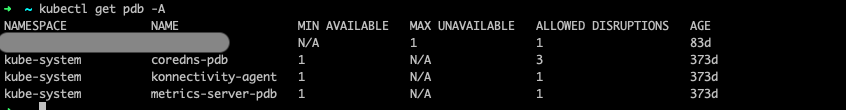
Run
kubectl get pdb -Aand checkALLOWED DISRUPTIONSis atleast 1 or higher as shown above. After verifying this, we can proceed with the draining of nodes.kubectl drain <node1> <node2> ... --ignore-daemonsets --delete-emptydir-dataNote: Using –delete-emptydir-data is required to evict the AKS-created coredns and metrics-server pods. If this flag isn’t used, an error is expected.
- Get all the nodes in
Run
k get pods -o wideand checkNODEcolumn if all the pods are rescheduled on to the new nodes innodepool-new.
This was a short yet precise guide on how to efficiently migrate to ephemeral OS disks in AKS. I hope you found it helpful.